Who Has The Poorest Country?
Have you ever wondered who has the poorest country in the world? It’s a question that sparks curiosity and prompts us to explore the economic landscapes of different nations. In this article, we will delve into the depths of global poverty and uncover which country holds the unfortunate title of being the poorest. So, put on your detective hat and join us on this quest for knowledge!
When it comes to measuring the poverty of a country, various factors come into play. GDP per capita, income inequality, unemployment rates, and access to basic necessities are just a few of the elements that paint a picture of a nation’s economic standing. By examining these indicators, we can gain insights into the struggles faced by different countries and the efforts being made to alleviate poverty. So, let’s dive into the data and discover who holds the unfortunate distinction of having the poorest country in the world. Get ready for a thought-provoking exploration of socioeconomic conditions and the challenges faced by nations in their quest for prosperity.
Who has the poorest country?
When it comes to determining the poorest country, it’s important to consider various factors such as GDP per capita, poverty rates, and overall economic conditions. According to recent data, some of the countries often considered to be among the poorest include Burundi, South Sudan, and Malawi. These nations face significant challenges in terms of poverty, inadequate healthcare, and limited access to education. However, it’s crucial to remember that poverty is a complex issue influenced by a range of factors.
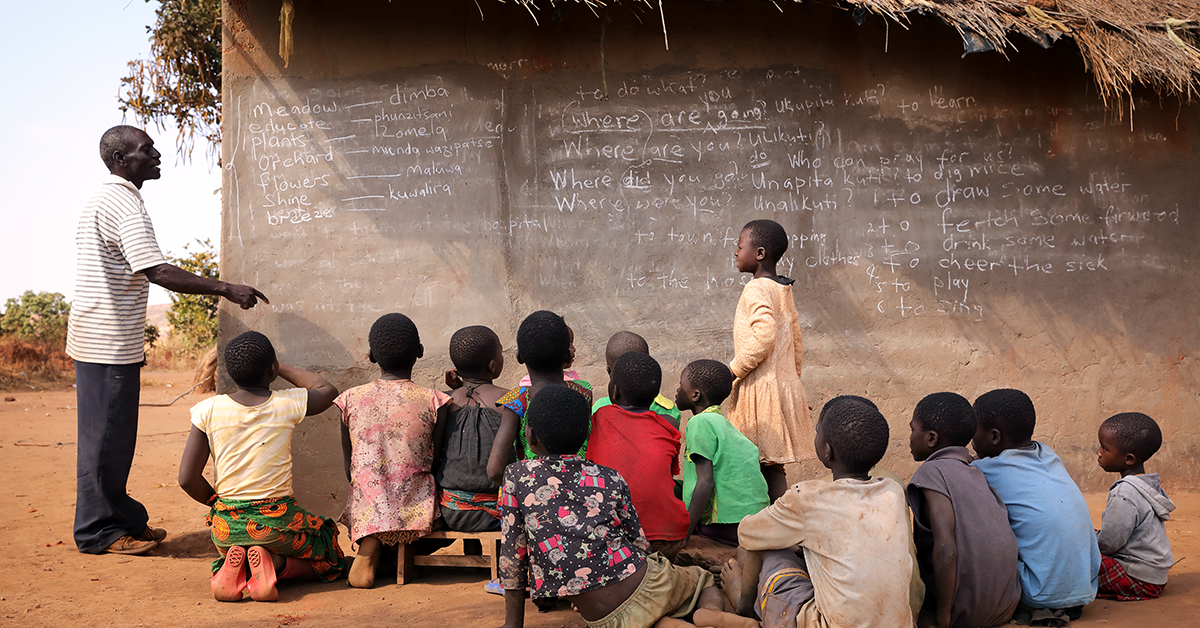
Who Has the Poorest Country?
Living in poverty is a reality for millions of people around the world. The distribution of wealth is vastly unequal, with some countries facing extreme poverty and economic challenges. In this article, we will explore the countries that are considered the poorest in the world and the factors contributing to their economic struggles. We will delve into the social, political, and economic factors that play a role in determining the poverty levels of these nations.
The Impact of Colonialism and Historical Factors
Many of the countries that are considered the poorest today have a history of colonization and exploitation. The effects of colonialism can still be felt in these nations, as they continue to struggle with the legacy of exploitation and economic dependency. The extraction of resources by colonial powers often left these countries impoverished and unable to develop sustainable economies.
Additionally, political instability and conflict have played a significant role in perpetuating poverty in these nations. Civil wars, corruption, and weak governance have hindered economic growth and development. The lack of infrastructure, education, and healthcare systems further exacerbate the poverty levels in these countries.
Political Factors
Corruption is a prevalent issue in many of the world’s poorest countries. When government officials misuse public funds for personal gain, it hampers development and perpetuates poverty. Lack of transparency and accountability in governance systems hinder economic growth and discourage foreign investment.
Moreover, conflicts and political instability also contribute to the poverty levels in these nations. Ongoing wars and civil unrest disrupt economic activities, displace populations, and divert resources away from development efforts. The lack of security and stability makes it difficult for businesses to thrive and for people to escape the cycle of poverty.
Economic Factors
Economic factors such as limited access to credit, high levels of unemployment, and lack of job opportunities further contribute to the poverty levels in these countries. The absence of a diversified economy often leaves these nations reliant on a few industries or agricultural sectors, making them vulnerable to fluctuations in global markets.
Income inequality is another significant economic factor that perpetuates poverty. A small elite class often controls the majority of wealth, while the majority of the population struggles to meet their basic needs. This unequal distribution of wealth prevents economic mobility and perpetuates the cycle of poverty.
The Poorest Countries in the World
Now let’s take a closer look at some of the poorest countries in the world. It’s important to note that poverty is a complex issue with multiple dimensions, and these countries face unique challenges that contribute to their economic struggles.
1. Burundi
Burundi, located in East Africa, is often ranked as one of the poorest countries in the world. Decades of political instability, ethnic conflict, and civil war have devastated the economy and hindered development. A lack of infrastructure, limited access to education and healthcare, and high levels of corruption contribute to the poverty levels in this nation.
2. Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is another country plagued by poverty. Despite being rich in natural resources, including minerals and timber, the country struggles with political instability, armed conflict, and corruption. The ongoing conflicts have displaced millions of people and hindered economic progress.
3. Malawi
Malawi, a landlocked country in southeastern Africa, faces numerous economic challenges. Limited access to education, healthcare, and infrastructure contribute to the poverty levels in this nation. Agricultural dependence and vulnerability to climate change also impact the country’s economic stability.
4. Niger
Niger, located in West Africa, is considered one of the poorest countries in the world. The country faces numerous challenges, including a high population growth rate, environmental degradation, and vulnerability to droughts. Limited access to education, healthcare, and infrastructure further contribute to the poverty levels in this nation.
5. Central African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR) is a country in Central Africa that has faced significant political instability and conflict. Decades of civil war and political unrest have left the country in a state of economic collapse. Lack of access to education, healthcare, and infrastructure contribute to the high poverty levels in the CAR.
Conclusion
The countries mentioned above represent just a few examples of the poorest nations in the world. It is crucial to address the underlying factors contributing to poverty, such as historical legacies, political instability, and economic challenges. By focusing on sustainable development, improving governance, and promoting equal opportunities, we can work towards reducing poverty and creating a more equitable world.
Key Takeaways: Who has the poorest country?
- Many factors contribute to a country’s poverty, such as political instability, lack of resources, and poor governance.
- According to the World Bank, the poorest country in the world is currently Burundi, a small country in East Africa.
- Poverty can have severe impacts on people’s lives, including limited access to education, healthcare, and basic necessities.
- International organizations and governments are working to alleviate poverty through various initiatives and aid programs.
- It is important to understand the complex causes of poverty and work towards sustainable solutions to uplift the poorest countries.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about the poorest countries in the world.
1. Which country is considered the poorest?
When it comes to measuring a country’s poverty, there are several factors to consider such as GDP per capita, income inequality, and access to basic resources. According to various reports, one of the countries often considered among the poorest is Burundi.
Burundi, located in East Africa, has faced numerous challenges including political instability, high population density, and limited access to basic services. Its economy heavily relies on agriculture, which is vulnerable to climate change and natural disasters, further exacerbating its poverty situation.
2. What are the main causes of poverty in the poorest countries?
The causes of poverty in the poorest countries are multi-faceted and interconnected. Some common factors include political instability, corruption, inadequate infrastructure, limited access to education and healthcare, and environmental challenges.
Political instability often hampers economic growth and development, making it difficult for these countries to attract investments and create job opportunities. Corruption further exacerbates the problem by diverting resources away from essential services and into the hands of a few individuals.
Inadequate infrastructure, such as poor transportation networks and limited access to clean water and sanitation, hinders economic development and the well-being of the population. Additionally, limited access to quality education and healthcare prevents individuals from breaking the cycle of poverty.
3. Are there any initiatives to alleviate poverty in the poorest countries?
Many international organizations and governments have implemented initiatives to alleviate poverty in the poorest countries. These initiatives focus on various aspects, including improving access to education, healthcare, and basic services, promoting sustainable economic development, and addressing governance and corruption issues.
For example, organizations like the World Bank and the United Nations have programs aimed at providing financial assistance, technical expertise, and policy guidance to help countries lift themselves out of poverty. Additionally, initiatives such as microfinance and social entrepreneurship have empowered individuals in poverty-stricken areas to start their own businesses and improve their livelihoods.
4. Can poverty in the poorest countries be eradicated?
Eradicating poverty in the poorest countries is a complex and long-term goal. However, with concerted efforts from governments, international organizations, and the global community, significant progress can be made.
Key strategies for poverty eradication include promoting inclusive economic growth, investing in education and healthcare, strengthening governance and institutions, and addressing the root causes of poverty. Sustainable development goals set by the United Nations provide a roadmap for tackling poverty and improving the well-being of people in the poorest countries.
5. How can individuals contribute to reducing poverty in the poorest countries?
Individuals can contribute to reducing poverty in the poorest countries through various means. One way is by supporting organizations and initiatives that work towards poverty alleviation, either through donations or volunteering.
Additionally, individuals can raise awareness about the issues faced by the poorest countries and advocate for policies that promote sustainable development, social justice, and equality. Supporting fair trade products, which ensure a fair income for producers in developing countries, is another way to contribute to reducing poverty.
THE POOREST COUNTRIES IN THE WORLD
Final Thought: Who Holds the Title for the Poorest Country?
After exploring the factors that contribute to a country’s poverty, it becomes clear that determining the poorest nation is not a straightforward task. Poverty is a complex issue that is influenced by a multitude of economic, political, and social factors. While some may argue that certain countries are the poorest based on specific metrics, it is important to approach this topic with nuance and recognize that poverty is multifaceted.
Instead of fixating on identifying the poorest country, it is more productive to focus on understanding the root causes of poverty and working towards sustainable solutions. It is crucial to address income inequality, lack of access to education and healthcare, political instability, and corruption, among other factors. By tackling these systemic issues, we can uplift communities and create a more equitable world.
In conclusion, poverty is a global challenge that requires collective efforts and innovative solutions. Rather than singling out a single country as the poorest, we should strive to address poverty as a global issue. By fostering collaboration, implementing effective policies, and promoting social and economic development, we can work towards alleviating poverty and creating a more equitable and prosperous future for all.